Benchmarking
Table of contents
We present two classification experiments performed using the 2019 version of the dataset to infer the main crop types present in each image. In the first experiment, static classification, we treated each individual image as a training instance (static image classification). In the second experiment, dynamic classification we explored the use of a temporal image series as an input.
Results
Static Classification
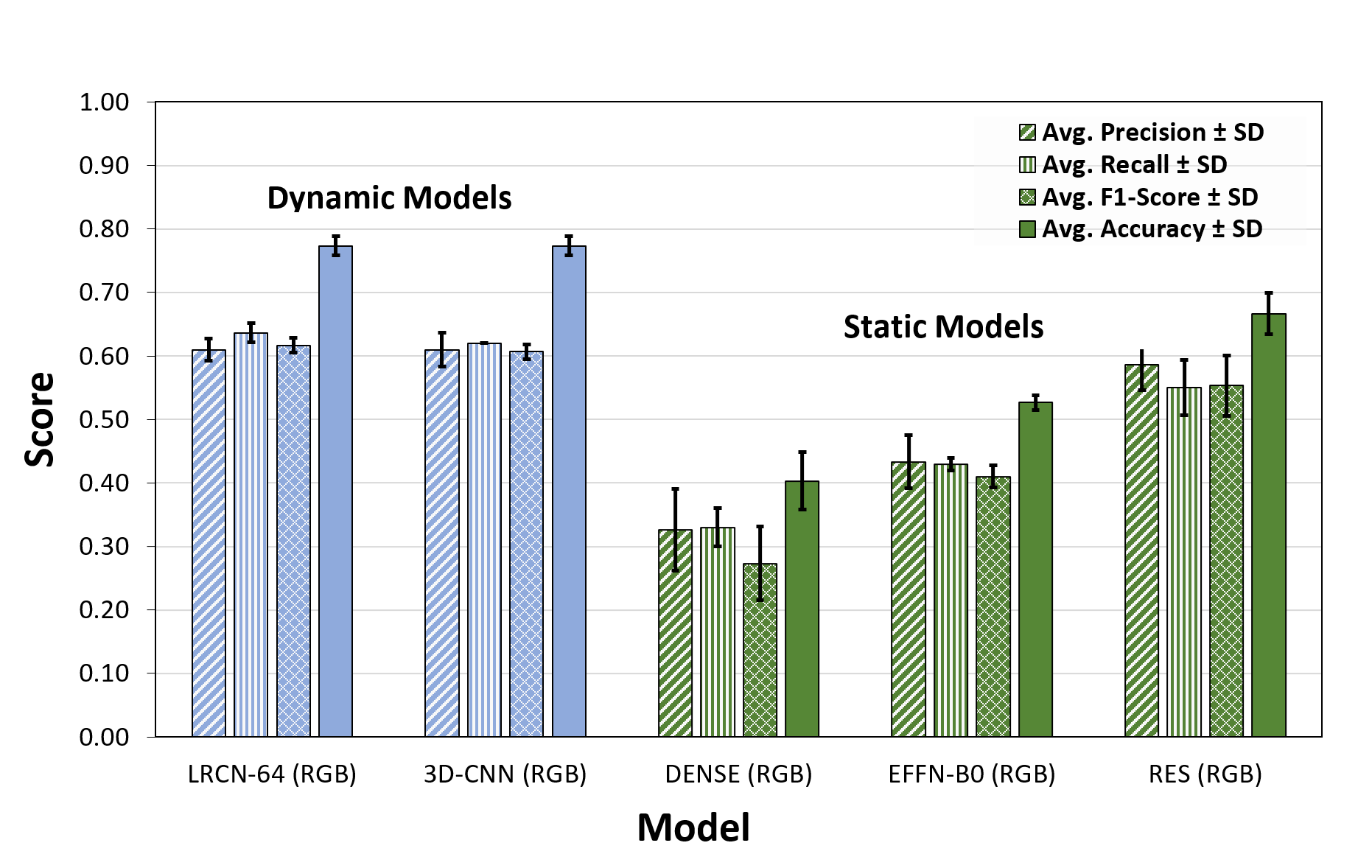
The deep learning models used for the static classification task include the ResNet-50, the DenseNet and the EfficientNet-B0.
| Models/Metrics | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DENSENET-121 (RGB) | 0.327 ± 0.064 | 0.330 ± 0.030 | 0.273 ± 0.058 | 0.403 ± 0.045 |
| EFFN-B0 (RGB) | 0.433 ± 0.042 | 0.430 ± 0.010 | 0.410 ± 0.017 | 0.527 ± 0.012 |
| RES-SCR (RGB) | 0.487 ± 0.021 | 0.473 ± 0.006 | 0.467 ± 0.012 | 0.577 ± 0.015 |
| RES (RGB) | 0.587 ± 0.040 | 0.550 ± 0.044 | 0.553 ± 0.047 | 0.667 ± 0.032 |
| DENSENET-121 (GNDVI) | 0.057 ± 0.029 | 0.133 ± 0.042 | 0.060 ± 0.044 | 0.150 ± 0.053 |
| EFFN-B0 (GNDVI) | 0.427 ± 0.015 | 0.430 ± 0.010 | 0.413 ± 0.015 | 0.527 ± 0.006 |
| RES (GNDVI) | 0.523 ± 0.067 | 0.423 ± 0.031 | 0.413 ± 0.040 | 0.523 ± 0.031 |
| DENSENET-121 (NDVI) | 0.217 ± 0.067 | 0.183 ± 0.015 | 0.140 ± 0.030 | 0.260 ± 0.026 |
| EFFN-B0 (NDVI) | 0.343 ± 0.055 | 0.310 ± 0.052 | 0.303 ± 0.046 | 0.400 ± 0.053 |
| RES-SCR (NDVI) | 0.280 ± 0.036 | 0.293 ± 0.012 | 0.257 ± 0.021 | 0.370 ± 0.026 |
| RES (NDVI) | 0.463 ± 0.031 | 0.410 ± 0.036 | 0.0413 ± 0.025 | 0.517 ± 0.025 |
| DENSENET-121 (NDVI45) | 0.187 ± 0.055 | 0.257 ± 0.035 | 0.180 ± 0.036 | 0.293 ± 0.032 |
| EFFN-B0 (NDVI45) | 0.470 ± 0.017 | 0.460 ± 0.010 | 0.443 ± 0.012 | 0.543 ± 0.006 |
| RES (NDVI45) | 0.480 ± 0.020 | 0.453 ± 0.015 | 0.443 ± 0.023 | 0.547 ± 0.021 |
| DENSENET-121 (OSAVI) | 0.213 ± 0.021 | 0.210 ± 0.044 | 0.153 ± 0.038 | 0.257 ± 0.051 |
| EFFN-B0 (OSAVI) | 0.493 ± 0.021 | 0.477 ± 0.006 | 0.463 ± 0.012 | 0.567 0.006 |
| RES (OSAVI) | 0.533 ± 0.060 | 0.530 ± 0.026 | 0.513 ± 0.040 | 0.617 ± 0.035 |
| DENSENET-121 (PSRI) | 0.160 ± 0.020 | 0.197 ± 0.015 | 0.147 ± 0.012 | 0.260 ± 0.017 |
| EFFN-B0 (PSRI) | 0.417 ± 0.029 | 0.393 ± 0.006 | 0.380 ± 0.010 | 0.483 ± 0.006 |
| RES-SCR (PSRI) | 0.333 ± 0.042 | 0.297 ± 0.029 | 0.277 ± 0.029 | 0.393 ± 0.006 |
| RES (PSRI) | 0.437 ± 0.046 | 0.397 ± 0.012 | 0.400 ± 0.017 | 0.483 ± 0.012 |
Dynamic Classification
The deep learning models used for the dynamic classification task include the 3 Dimensional Convolutional Network (3DCNN) and the Long-Term Recurrent Convolutional Networks (LRCN).
| Models/Metrics | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRCN-64 (RGB) | 0.610 ± 0.017 | 0.637 ± 0.015 | 0.617 ± 0.013 | 0.774 ± 0.014 |
| 3D-CNN (RGB) | 0.610 ± 0.026 | 0.620 ± 0.000 | 0.607 ± 0.012 | 0.773 ± 0.012 |
| LRCN-64 (GNDVI) | 0.030 ± 0.000 | 0.100 ± 0.000 | 0.040 ± 0.000 | 0.277 ± 0.006 |
| 3D-CNN (GNDVI) | 0.287 ± 0.085 | 0.250 ± 0.066 | 0.200 ± 0.069 | 0.313 ± 0.067 |
| LRCN-64 (NDVI) | 0.030 ± 0.000 | 0.100 ± 0.000 | 0.040 ± 0.000 | 0.270 ± 0.000 |
| 3D-CNN (NDVI) | 0.360 ± 0.064 | 0.373 ± 0.093 | 0.347 ± 0.104 | 0.470 ± 0.100 |
| LRCN-64 (NDVI45) | 0.123 ± 0.162 | 0.180 ± 0.139 | 0.127 ± 0.150 | 0.313 ± 0.101 |
| 3D-CNN (NDVI45) | 0.467 ± 0.065 | 0.387 ± 0.031 | 0.377 ± 0.040 | 0.530 ± 0.026 |
| LRCN-64 (OSAVI) | 0.140 ± 0.191 | 0.163 ± 0.110 | 0.117 ± 0.133 | 0.300 ± 0.087 |
| 3D-CNN (OSAVI) | 0433 ± 0.151 | 0.447 ± 0.136 | 0.417 ± 0.153 | 0.570 ± 0.114 |
| LRCN-64 (PSRI) | 0.450 ± 0.010 | 0.467 ± 0.012 | 0.453 ± 0.012 | 0.563 ± 0.012 |
| 3D-CNN (PSRI) | 0.447 ± 0.040 | 0.350 ± 0.087 | 0.347 ± 0.087 | 0.477 ± 0.078 |
The LRCN and 3D-CNN architectures showed higher average accuracies (0.77 for both models). Our overall results showed that classifiers trained with the triplets outperformed the static models (10% increase in accuracy, 0.773 vs 0.667, p<0.05). Furthermore, more complex models (≥ 5.38 millions of parameters) underperformed in contrast to the 3D-CNN (around 31,000 parameters).
Use Cases
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry’s standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.